Multi-level marketing pyramid often referred to as network marketing or pyramid selling, is a business model that relies on a network of distributors to sell products or services directly to consumers. In this model, distributors earn commissions not only for their own sales but also for the sales made by the distributors they recruit into the network.
While Multi-level marketing pyramid has been praised for its potential to offer flexible earning opportunities and entrepreneurial freedom, it has also faced criticism and controversy due to its resemblance to illegal pyramid schemes.
This article delves into the concept of multi-level marketing pyramids, exploring their structure, operations, controversies, and regulatory oversight.
Historical Background

Multi-level marketing pyramid has its roots in the mid-20th century, with its origins traced back to the United States. While the concept of direct selling and network marketing has existed for centuries, the modern MLM model emerged in the 1940s and 1950s with the establishment of companies like Nutrilite and Amway.
Nutrilite, founded in 1934 by Carl Rehnborg, is often credited as one of the pioneers of MLM. Rehnborg’s vision was to distribute nutritional supplements through a network of independent distributors, who would earn commissions not only from their own sales but also from the sales made by distributors they recruited.
Amway, founded in 1959 by Rich DeVos and Jay Van Andel, further popularized the Multi-level marketing pyramid model. Amway expanded its product line beyond nutritional supplements to include household and personal care products.
The company’s success and global expansion contributed to the rapid growth of the MLM industry.
Throughout the latter half of the 20th century, Multi-level marketing pyramid companies proliferated, offering a wide range of products and services, including cosmetics, health and wellness products, and household goods.
The industry saw periods of both exponential growth and controversy, with MLM companies facing scrutiny over their business practices and allegations of operating as illegal pyramid schemes.
Despite challenges and regulatory hurdles, MLM continued to evolve and adapt, with companies refining their compensation plans, marketing strategies, and distributor training programs.
The rise of the internet and social media further transformed the MLM landscape, providing distributors with new tools and platforms to reach customers and build their networks.
Today, MLM remains a significant industry worldwide, with thousands of companies operating in diverse sectors and markets.
While it continues to attract entrepreneurs seeking flexible earning opportunities and the potential for financial success, Multi-level marketing pyramid also continues to face skepticism and criticism from regulators, consumer advocacy groups, and the general public.
MLM Companies In USA: Comprehensive Guide
Structure of Multi-level marketing Pyramids
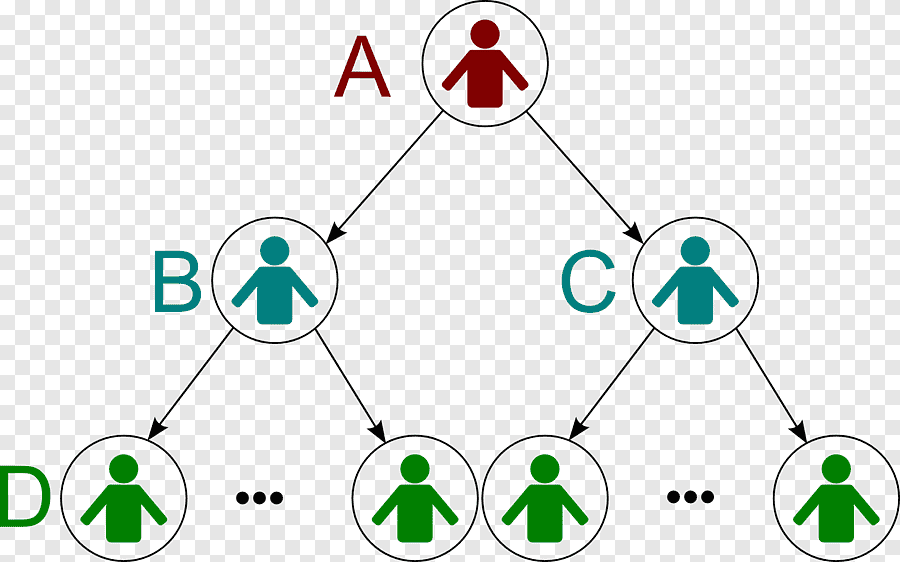
Multi-level marketing pyramid typically have a hierarchical structure that resembles a pyramid, with multiple levels of distributors organized under a central company or parent organization. The structure consists of several key components:
-
Company or Parent Organization:
At the top of the pyramid is the Multi-level marketing pyramid MLM company or parent organization, which develops and manufactures the products or services being sold.
This entity is responsible for setting the compensation plan, providing marketing materials, and overseeing the overall operations of the MLM business.
-
Distributors:
The next level of the pyramid consists of individual distributors who join the Multi-level marketing pyramid program to sell the company’s products or services.
These distributors may purchase products at wholesale prices and then resell them at retail prices, earning a profit on each sale. They are also responsible for recruiting new distributors into their downline.
-
Downline:
As distributors recruit new members into the MLM program, they build a downline organization consisting of their recruits and subsequent generations of distributors.
Each distributor in the downline is considered part of the recruiting distributor’s network and contributes to their potential earnings.
-
Uplines:
Distributors who recruit new members into the Multi-level marketing pyramid program are referred to as uplines.
They serve as mentors and leaders for their downline distributors, providing guidance, support, and training to help them succeed in their MLM businesses.
Uplines also earn commissions on the sales made by their downline distributors.
-
Levels or Tiers:
Multi-level marketing pyramid typically have multiple levels or tiers of distributors, each representing a generation within the downline organization.
As distributors recruit new members and those members recruit others, the downline organization grows deeper, with each level potentially generating additional commissions for the distributors at higher levels.
-
Commission Structure:
MLM companies often employ complex commission structures that reward distributors for both their own sales and the sales made by their downline organization.
Commissions may be paid out based on various factors, including product volume, rank advancements, and team performance.
Overall, the structure of Multi-level marketing pyramid is designed to incentivize recruitment and sales growth, with distributors encouraged to build and expand their networks to increase their earning potential.
However, this hierarchical structure has drawn criticism and scrutiny, with some alleging that it closely resembles an illegal pyramid scheme.
As a result, Multi-level marketing pyramid companies must navigate regulatory requirements and legal challenges to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Operations of Multi-level marketing Pyramids
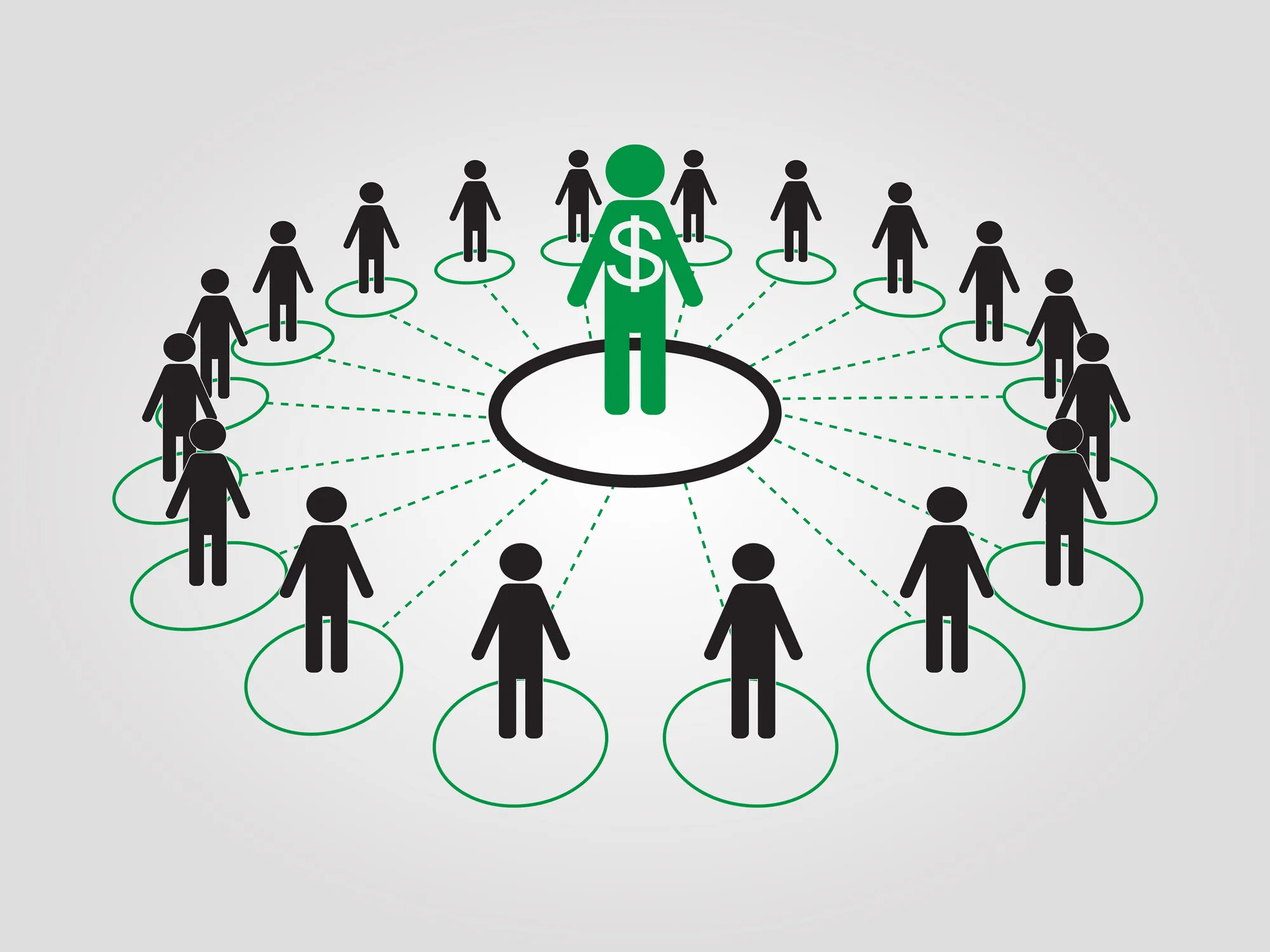

The operations of Multi-level marketing pyramid involve various activities and strategies aimed at driving sales, recruiting new distributors, and maximizing earnings for participants. These operations typically include the following key components:
-
Product or Service Sales:
Multi-level marketing pyramid companies offer a range of products or services that distributors promote and sell to consumers.
Distributors may utilize various sales channels, including face-to-face interactions, online platforms, and social media, to reach potential customers and generate sales.
They earn commissions on the products or services they sell, often at retail prices.
-
Recruitment Practices:
A significant aspect of MLM operations involves recruiting new distributors into the network. Existing distributors actively seek out potential recruits and promote the opportunity to join the Multi-level marketing pyramid program.
They may emphasize the potential for flexible earning opportunities, personal development, and entrepreneurial freedom to attract new members.
Recruitment efforts often focus on expanding the distributor’s downline organization to increase earning potential.
-
Training and Support:
MLM companies provide training and support to their distributors to help them succeed in their businesses. This may include educational materials, online resources, webinars, and in-person training sessions designed to enhance product knowledge, sales skills, and business acumen.
Experienced distributors, known as uplines, play a crucial role in mentoring and supporting new recruits, offering guidance and advice on building and growing their businesses.
-
Marketing and Promotion:
MLM distributors are encouraged to engage in marketing and promotional activities to attract customers and recruit new members. This may involve creating marketing materials, such as brochures, flyers, and social media posts, to showcase products or promote the Multi-level marketing pyramid opportunity.
Distributors may also participate in company-sponsored events, trade shows, and networking meetings to expand their reach and connect with potential customers and recruits.
-
Compensation and Rewards:
MLM compensation plans are designed to incentivize both product sales and recruitment efforts. Distributors earn commissions on their own sales, as well as bonuses and incentives for building and growing their downline organizations.
Compensation structures often include various tiers or ranks, with higher-ranking distributors eligible for increased earnings and additional rewards, such as cash bonuses, trips, and other incentives.
Overall, the operations of Multi-level marketing pyramid revolve around driving product sales, recruiting new distributors, and providing training and support to facilitate success for participants. While MLM offers potential opportunities for flexible earning and entrepreneurship, it is important for participants to carefully evaluate the business model and understand the potential risks and challenges involved.
Controversies and Criticisms
Controversies and criticisms surrounding Multi-level marketing pyramid often stem from concerns about their business practices and ethical implications.
One of the primary criticisms is that MLM companies operate in a manner that closely resembles illegal pyramid schemes.
In pyramid schemes, participants primarily earn money by recruiting new members rather than selling legitimate products or services. This focus on recruitment can lead to unsustainable business models where the majority of participants incur financial losses.
Additionally, there have been allegations that some Multi-level marketing pyramid companies engage in deceptive or misleading marketing tactics to lure individuals into joining their programs.
This may include exaggerating potential earnings, making false promises about the benefits of participation, or downplaying the risks involved.
Such practices can result in disillusionment and financial hardship for participants who fail to achieve the promised rewards.
Another criticism of MLM is the emphasis on recruiting new distributors over selling products or services.
This recruitment-focused model can create a relentless pursuit of new recruits, sometimes at the expense of providing genuine value to consumers.
Critics argue that this focus on recruitment can lead to the exploitation of vulnerable individuals who may be persuaded to invest time and money in a venture with limited potential for success.
Furthermore, Multi-level marketing pyramid companies have faced legal scrutiny and regulatory challenges in various jurisdictions.
Some MLM business practices have been found to violate consumer protection laws or regulations governing pyramid schemes.
As a result, MLM companies may face fines, lawsuits, or even regulatory sanctions if found to be operating unlawfully.
Overall, while MLM pyramids have attracted participants with promises of financial freedom and entrepreneurial opportunities, they have also been met with skepticism and criticism due to concerns about their business practices, ethics, and legality.
It is essential for individuals considering involvement in MLM to thoroughly research and evaluate the risks and benefits before making any commitments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Multi-level marketing pyramid represent a complex and controversial business model that has elicited both enthusiasm and skepticism.
While proponents of MLM praise its potential for offering flexible earning opportunities and entrepreneurial freedom, critics argue that the emphasis on recruitment over product sales can lead to unsustainable business practices and financial losses for participants.
Despite the controversies and criticisms surrounding MLM, the industry continues to thrive, with thousands of companies operating worldwide and millions of individuals participating as distributors.
However, regulatory scrutiny and legal challenges persist, highlighting the need for greater transparency, accountability, and consumer protection within the MLM industry.
Other Questions
- What is a Multi-level marketing pyramid?
A multi-level marketing pyramid is a business model where participants earn commissions not only for their own sales but also for the sales made by distributors they recruit into the network.
- What are some criticisms of Multi-level marketing pyramid?
Criticisms of MLM pyramids include concerns about their resemblance to illegal pyramid schemes, deceptive marketing practices, and the emphasis on recruitment over product sales.
- What are some key components of Multi-level marketing pyramid structure?
Key components of MLM pyramid structure include the company or parent organization, distributors, downline organization, uplines, levels or tiers, and commission structure.
- How do Multi-level marketing pyramid operate?
MLM pyramids operate by promoting products or services through a network of distributors who earn commissions on sales and recruit new members into the network.